10 Signs To Recognize And Address ADHD and Depression In Adults
Do you know, according to Forbes, an estimated 8.7 million adults have ADHD in the U.S.? Globally, the number of AdHD for adult is around 139.8 million!
Unfortunately, although these numbers are continuously rising, the signs of ADHD remain challenging to spot.
ADHD for adult can be challenging to diagnose since the symptoms tend to be more subtle or confused with other mental health conditions.
The indicators of ADHD, whether it's forgetfulness or attention deficiency, can pose complex challenges in adulthood. It can negatively affect your relationships and cause you to miss opportunities at work.
Without a required support, you may even experience memory loss and struggle to complete simple daily tasks at home. On top of that, countless researchers have found a strong link between undiagnosed ADHD depression.
Luckily, by recognizing ADHD signs early on, you can prevent the condition from getting worse and take back control of your life.
To help you, today's blog presents the most common signs of ADHD and depression in adults. We discuss the connection between the two disorders, how they may impact your life, and more.
What Is ADHD?
ADHD, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, is a neurodevelopmental condition affecting several executive functions. It can affect your ability to plan, organize, regulate emotions, control impulses, and pay attention.
Although many believe that ADHD only occurs in children and resolves on its own, that is a myth.
Once a person develops ADHD, it remains with them in some capacity, even when they have become adults. However, you can learn to manage the condition, adopt habits that minimize its effects, and receive ADHD therapy for adults to address the symptoms.
Also, it's common for the symptoms of ADHD to change over time. They can become less recognizable as you become older and cause you to become more vulnerable to other mental conditions.
Over time, ADHD in adults can cause you to become overwhelmed by day-to-day commitments, become hyper-focused on some projects, and make you lose track of time. You may also experience problems managing emotions, prioritizing and structuring tasks, and becoming sensitive to rejection.
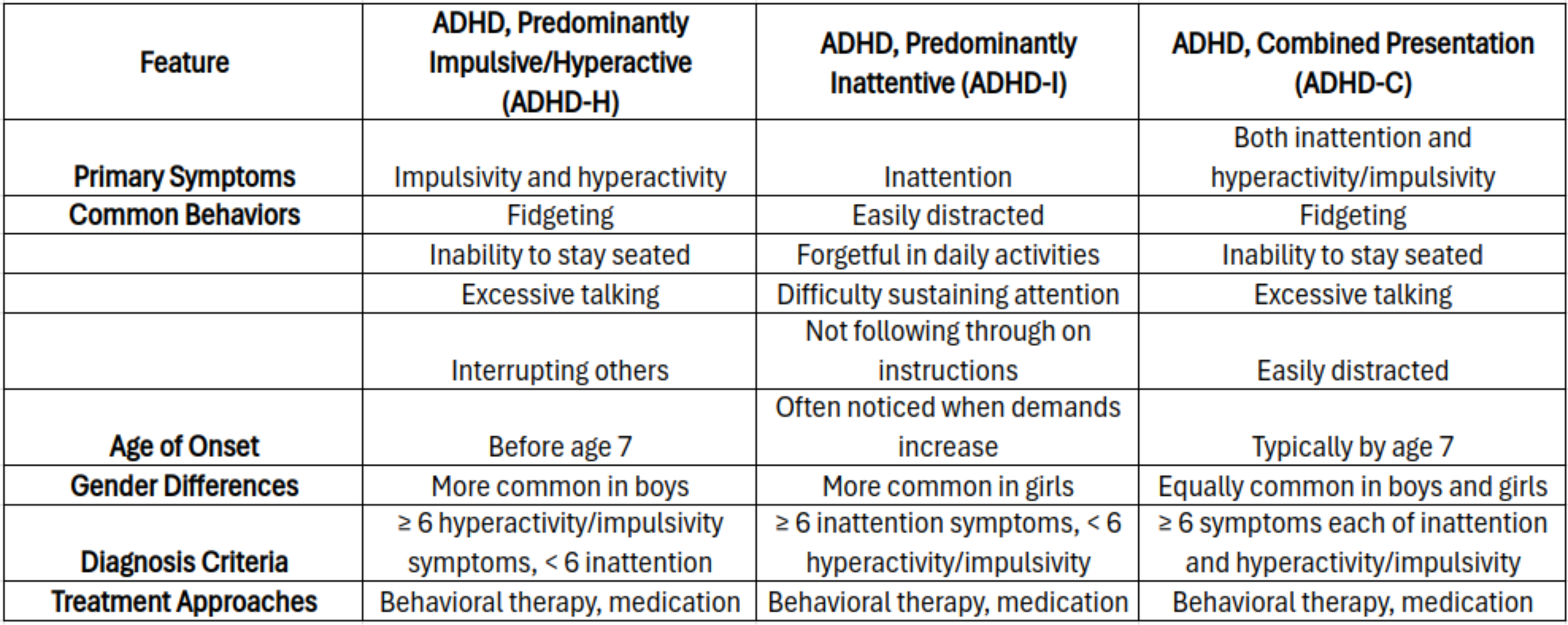
Types Of ADHD In Adults
The effects of adult ADHD symptom can vary from person to person, which means ADHD treatment options can also be different for two people. Depending on the type of ADHD you have, you might be hyper-focused, inattentive, or both.
Generally, there are three types of ADHD, divided based on their impacts. Below, we discuss each of them to help you understand the disorder.
Types of ADHD and Their Classifications
ADHD, predominantly impulsive/hyperactive
People who experience hyperactive ADHD type tend to display impulsive behavior and don't show signs of being inattentive.
The most common signs of hyperactive/impulsive type of ADHD include:
Feeling restless
Always on the move
Constantly leaving their seat even when it's unnecessary or they should be seating
Interrupting others or cutting into their conversations
Fidgeting when seated
Having trouble waiting for their turn
Taking over other's activities
ADHD, predominantly inattentive
As the name suggests, this ADHD type causes individuals to exhibit signs of inattentiveness. It makes it difficult for individuals to stay focused on a task and pay attention.
If you suffer from this ADHD type, you are likely to spot the following signs.
Having trouble organizing things
Quickly losing focus
Constantly having unrelated, distracting thoughts
Avoiding tasks that demand you to focus
Getting easily distracted during conversations
Forgetting to complete a task
Struggling to manage time
Overlooking significant details
Making silly errors
Misplacing items
Having trouble memorizing things
ADHD, combined presentation
It the most common type of ADHD in adults that causes an individual to show impulsive and hyperactive behaviors. At the same time, the combined ADHD type can make someone extremely easy to distract.
When it comes to ADHD for adults, experts recommend personalizing the ADHD treatment options and coping strategies based on individual symptoms. Furthermore, ADHD can manifest distinctly in males and females. Adult ADHD symptom in women are often underdiagnosed. Therefore, personalization is even more necessary.
What Is Depression?
Major depressive disorder or clinical depression is a classification of a mood disorder. As one of the most common mental illnesses, depression affects around 8.4% (21 million) of American adults.
It causes persistent loss, sadness, anger, and a loss of interest. When left untreated, depression can negatively affect how you feel mentally and physically. It can influence your thoughts and behaviors and make it hard to complete everyday tasks.
Depression can also worsen existing mental or physical conditions, including arthritis, asthma, diabetes, obesity, cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
Contrary to popular belief, depression is more than just sadness or grief. Grief usually refers to the emotions you feel after a traumatic life event or losing a loved one. It's a combination of emotional pain and happy memories. Depressive disorder, however, involves feelings of sadness or a low persistent mood lasting for some time.
With psychotherapy and medication, most people can manage the symptoms of depression.
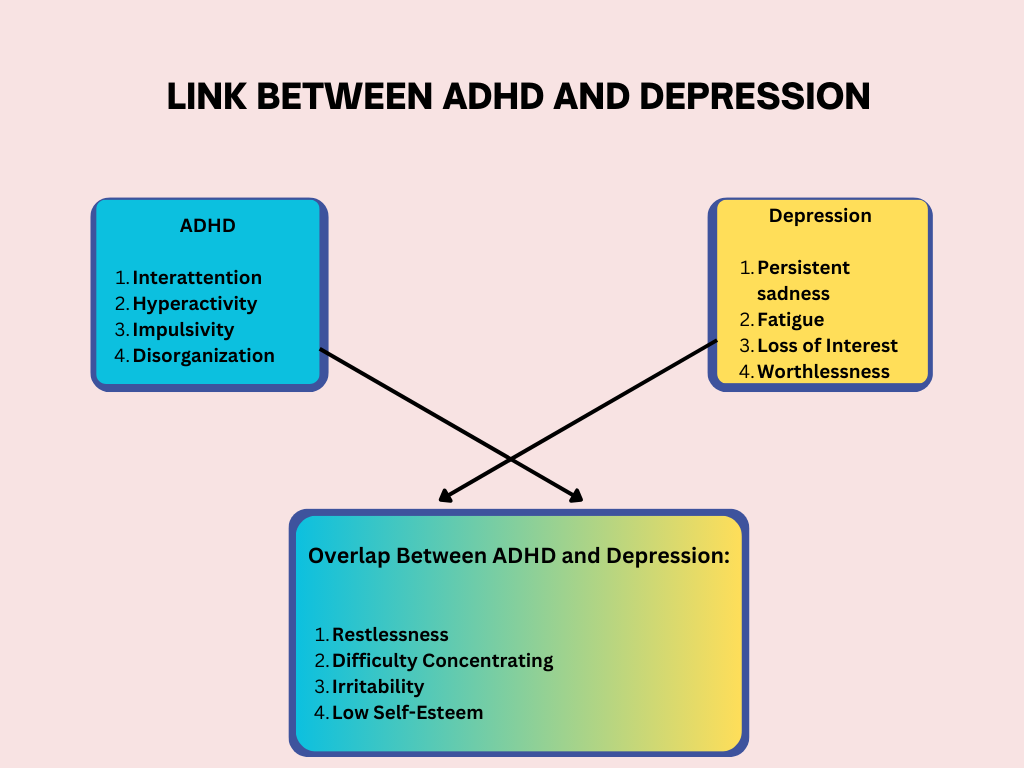
What Is The Link Between ADHD And Depression?
Link Between ADHD and Depression
Although ADHD and depression are separate conditions, they are frequently connected. Research estimates that one in three people who have ADHD have experienced depression.
Researchers from the University of Chicago have found that children or adolescents with ADHD are almost ten times more likely to develop depression compared to those who don't have ADHD.
While the precise reason behind this connection is unclear, there is some noticeable overlap between the symptoms of these two disorders. For instance, both ADHD and depression are comprised of loss of motivation and difficulty concentrating. However, the reason behind the symptoms can be different.
To give you an example, an individual suffering from ADHD may lack motivation due to being inattentive. They wish to focus and complete a task but struggle to focus on the details. On the other hand, a person with depression may lack motivation because they feel fatigued and believe there's no purpose.
Experts refer to the overlapping of depression and ADHD as comorbid conditions. It means when you have one, there's a good chance you will also have the other one.
Various factors can affect this condition, including how someone manages their unhelpful thoughts, awareness of their feelings, and goal-oriented behavior.
Causes Of Depression In People With ADHD
Causes Of Depression in People with ADHD
With so many statistics establishing a link between ADHD and depression, you might question- whether ADHD can cause depression.
While the subject requires much more research, in some cases, ADHD has led to depression. When people have a hard time managing their ADHD symptoms, they may start to get depressed. Adults may face trouble at work or struggle to maintain relationships. The issues can lead to intense feelings of hopelessness.
Doctors have also found a link between ADHD, depression, and family history. People who have been diagnosed with ADHD or depression likely have a family member with the same condition.
These are some other factors that can explain why people with ADHD have a high risk of developing depression:
ADHD and depression are physically and mentally exhausting
Functioning as a neurodiverse person in a neurotypical world can make you feel overwhelmed, misunderstood, and alone
Genetics and family history
The stigmatizing nature of ADHD
Factors that make you more vulnerable to developing depression if you already have ADHD are
Being a female
Having inattentive ADHD type
Having an early childhood diagnosis of the condition
Not treating ADHD
If your mother suffered from depression during her pregnancy with you
10 Common Signs of ADHD And Depression In Adults
People with co-existing depression and ADHD struggle much more than those with either disorder. That's why it's essential to recognize the signs early and get professional help to manage the symptoms. With the right therapist by your side, you can soon start to make progress and feel better. On the flip side, if you leave the conditions unaddressed, it can lead to more psychological and physical complications.
Here, we list the most common signs of ADHD and depression in adults to help you understand the depth of your issues.
1. Scattered Focus
Scattered focus is a telltale sign of ADHD. It goes beyond finding it hard to pay attention. When you have ADHD, depression, and lack of focus, you are easily distracted, you find it hard to stay engaged in conversations, and you may fail to complete projects or tend to overlook details. ADHD can also cause you to daydream and zone out amid a task.
As depression tends to take the pleasure out of things you used to love, you may lose interest and focus. Loss of focus can also be a result of exhaustion caused by depression. Losing interest and focus is common in both ADHD and depression in adults.
2. Disorganization Chaos
Everyone faces challenges in life. However, when you have Adult ADHD, anxiety, or depression, overcoming those challenges can feel like an impossible endeavor.
ADHD can make it difficult for you to keep everything in order. You may face issues with organizational skills, including keeping track of tasks and logically prioritizing them.
Similarly, depression can make it challenging for you to concentrate. Due to the lack of energy, motivation, and hopelessness, you may start neglecting yourself and your surroundings. Tidying up can become an impossible task when you are feeling low.
3. Impulsive Decisions
When you have ADHD, impulsive decisions can manifest in multiple ways. You may catch yourself interrupting others, speeding through tasks, being socially improper, and acting without considering the consequences.
The link between depression and impulsiveness, however, is a bit more complicated. Since depression causes low levels of dopamine, which is a neurotransmitter part of the brain's reward system, you may engage in impulsive behavior to get a brief rush of dopamine, as it can bring you a few moments of joy.
4. Restless Energy
Being restless and anxious is another common sign of ADHD and depression in adults. You may observe it in a variety of ways, including:
Flight of thoughts
Impulsive behaviors
Trouble sitting still
Fidgeting
Catastrophizing
Overthinking
People often misinterpret fidgeting as inattention. However, in adults, fidgeting can be an attempt to stay focused when a task isn't stimulating enough.
Furthermore, anxiety often similarly accompanies depression and causes the patient to experience
Nervousness, stress, and restlessness
Panic
Rapid breathing and heart rate
Muscle twitching
Trouble focusing
Heavy sweating
5. Memory Mishaps
ADHD and depression in adults can cause memory loss. ADHD mainly affects short-term or working memories and can cause you to:
Forget things on your grocery list
Leave essential items at home
Reread sections due to not being able to memorize information
Lose track of belongings
Face difficulty following instructions
When you have ADHD, your brain tends to encode information in a disorganized way. On the other hand, if you have depression alongside ADHD, it may impact your long-term memory as well.
Depression can physically impair parts of your brain that help retain memories. It can even result in cognitive impairment.
6. Low Mood Blues
It's natural to feel unmotivated when you constantly struggle to complete daily, straightforward tasks. If you have ADHD and depression, you are likely to procrastinate as well. You may face sleep problems, which increases the feeling of tiredness and creates a vicious cycle of feeling low.
It's also common for depressed people to feel worthless or guilty. Thankfully, with the correct ADHD and depression treatment, you can learn how to cope with these feelings positively.
7. Lost Interest
As mentioned, withdrawing from activities is one of the most common signs of depression. The absent-mindedness caused by ADHD can enhance this attribute and make things feel even duller.
Lack of interest can trouble your relationships with family, friends, colleagues, and partners. You may forget significant events, like anniversaries or birthdays, isolate yourself from others, and fail to fulfill responsibilities.
8. Sleep Disruptions
Part of the reason that people suffering from ADHD and depression withdraw from socializing and other activities is the constant feeling of drowsiness. The overwhelming sense of lethargy and lack of energy can, on one hand, lead to excessive sleeping and, on the other, result in insomnia.
The disruptive sleep cycles feed off each other and result in anxiety and overthinking.
9. Fatigue and Low Energy
ADHD and depression in adults can cause people to neglect their physical health.
From lousy sleep habits and lack of exercise to an imbalanced diet, the countless effects of depression and ADHD can make you constantly feel low on drive. If you don't have a support system to understand the symptoms and help you through, your physical health can deteriorate even further.
10. Unhelpful Self-Talk
While depression can impact an individual's self-esteem, ADHD can cause patients to be hypercritical of them. It can result in a lot of unhelpful self-talk. As the conditions influence your relationships and work, your self-image can deteriorate. You can view every difficulty in your life as a personal failure or underachievement and put yourself under excessive pressure.
The Triggers of ADHD in Adult Life
ADHD and depression in adults remain chronically underdiagnosed, especially in women. You may have lived with undiagnosed ADHD for years before the symptoms started to surface after a challenging life event.
Although ADHD doesn't have a cure, you can learn to manage it to reduce its impact on your life by identifying the triggers. Once you know what triggers your hyperactive or inattentive behavior, you can take steps to make better lifestyle choices.
1. Poor Sleep
Surveys reveal that about 50% of people diagnosed with ADHD experience sleep problems. Alongside the ADHD and depression link, experts have also found ADHD symptoms overlap with sleep deprivation.
Not getting adequate sleep can make anyone feel sluggish. However, when you are already living with ADHD, not getting at least 7 to 8 hours of sleep can worsen your health.
You may face issues like
Inattention
Hyperactivity
Careless blunders
Forgetfulness
Poor impulse control
Drowsiness
Performance issues
Trouble focusing and understanding
Slowed reaction time
2. Stress
Going through stressful events can trigger adult ADHD symptom. On the other hand, living with ADHD can put you in a constant state of stress. Researches indicate the main reason behind this is stress and ADHD both affect the exact location of the brain, the prefrontal cortex.
Filtering out excess stimulation becomes challenging as well when you have ADHD, which increases stress levels. Hence, therapists recommend incorporating stress management techniques into your daily habits. Additionally, consider taking small breaks from tasks, practicing meditation for relaxation, and exercising.
3. Overstimulation
Getting a bout of sensory overload is a common occurrence in ADHD and depression in young adults. It occurs when one or multiple of your senses become overstimulated, such as strong smells, loud sounds, flashing lights, specific tastes, and sudden touch.
Overstimulation can make it hard for your brain to grasp the situation. Therefore, it can be helpful to try to avoid overstimulation when possible.
4. Technology
Electronic devices like smartphones, television, and computers can also overstimulate your brain. A study done in 2019 found that more than 2 hours of screen time per day can significantly increase inattention in children. While these practices don't cause ADHD, if you are already living with it, excessive screen time can exaggerate the symptoms.
5. Medical Conditions and Medications
Some medical conditions, such as sleep apnea, hypoglycemia, untreated diabetes, seizure disorders, and thyroid disease, can worsen the symptoms of ADHD and depressive disorder.
Additionally, some medications can do the same to ADHD patients, including sleep aids and beta blockers.
The Impact Of ADHD And Depression On Adults
Several studies have indicated that of all adults with ADHD, less than 20% are aware of their condition. Only a fourth of those who know about their condition are getting treatment.
Living with undiagnosed ADHD and depression is highly challenging.
It may feel impossible to stay organized, memorize things, or stick to a job. Juggling ADHD and relationships and completing daily tasks, such as getting up early in the morning, can feel like a battle.
Adults with ADHD and depression symptoms also tend to have a history of problems with relationships, school, and work. It's also common for adults with ADHD to always seem restless. If you have ADHD and depression, you may prefer quick fixes over longer steps that may give you greater rewards.
In addition to the psychological and emotional struggles, mental illnesses like depression can significantly affect an individual's physical health. Depression, mainly, is well-known for causing trouble to the digestive system. It can cause stomachaches, constipation, malnutrition, and cramps.
When left untreated, depression can bring down the health of your cardiovascular and immune systems.
You may feel irritated and angry, experience headaches, and lose interest in things. That's why it's essential to note your behavior and emotions. If you find anything troubling, refer to a trusted therapist immediately.
How Does Therapy And Counseling Help In ADHD And Depression?
Therapy and counseling are among the most effective ADHD and depression treatment methods. It's often the first line of treatment recommended by experts.
ADHD therapy for adults offers a structured environment where you can learn about the disorder, how it affects your life, and how to manage the symptoms. You will learn time management skills, anger management techniques, and organization strategies. Therapy will help you engage in self-care activities and improve your productivity and relationships.
Moreover, your counselor can use different types of therapies to tailor the treatment based on your struggles. For instance, ADHD Cognitive Behavioral Therapy can help alter your thoughts, behaviors, and attitude to better manage everyday situations.
Furthermore, other types of therapy, such as interpersonal therapy, can help you manage your relationships better. If you have trouble with social interaction, this type of therapy can be highly effective.
So, in a nutshell, getting therapy from a qualified expert for ADHD and depression can help
Improve your communication, organization, and management skills
Reduce the risk of medication side effects
Develop coping skills for overstimulating and stressful situations
Reduce the impact of ADHD and depression on your overall physical and mental health
Deliver you tailored support and advice
Take Control Of Your Mental Health With Snead Psychological Services
If you have ADHD, there's a good chance that you might develop depression as well. ADHD and depression in adults are, unfortunately, quite common and greatly undiagnosed. Hence, if you resonate with the above symptoms, refer to a qualified, experienced, and trusted therapist, such as Snead Psychological Services.
I help adults cope with various psychological and social challenges through personalized, one-on-one, individual counseling and therapy. Employing tested and proven methods, such as CBT, we can help you overcome your struggles in a safe, judgment-free space.
So, reach out today!